What is Vitamin B12, and why is it essential for the body?

Vitamin B12, also called Cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin that must be obtained from food, supplements, or fortified goods because the body is unable to produce its own. Despite being needed in trace levels, it is essential for maintaining the body’s proper function.
Because vitamin B12 is mostly stored in the liver and absorbed in the small intestine with the aid of a protein known as intrinsic factor, deficient appear gradually. This vitamin helps avoid tingling or numbness in the hands and feet and is necessary for a healthy nervous system.
Additionally, it helps you feel cognitively bright by promoting mental clarity, memory, and focus.
Why Vitamin B12 Deficiency Is So Common in India?
In addition to food, poor absorption caused by infections, acidity difficulties, or gut health concerns can lower vitamin B12 absorption. The body’s capacity to absorb this vitamin declines with age. Lifestyle habits such as chronic stress, smoking, and alcohol consumption further worsen the problem. Vitamin B12 absorption may also be hampered by long-term use of several medications, such as diabetes medications and antacids.
Common Symptoms of Vitamin B12 Deficiency You Shouldn’t Ignore
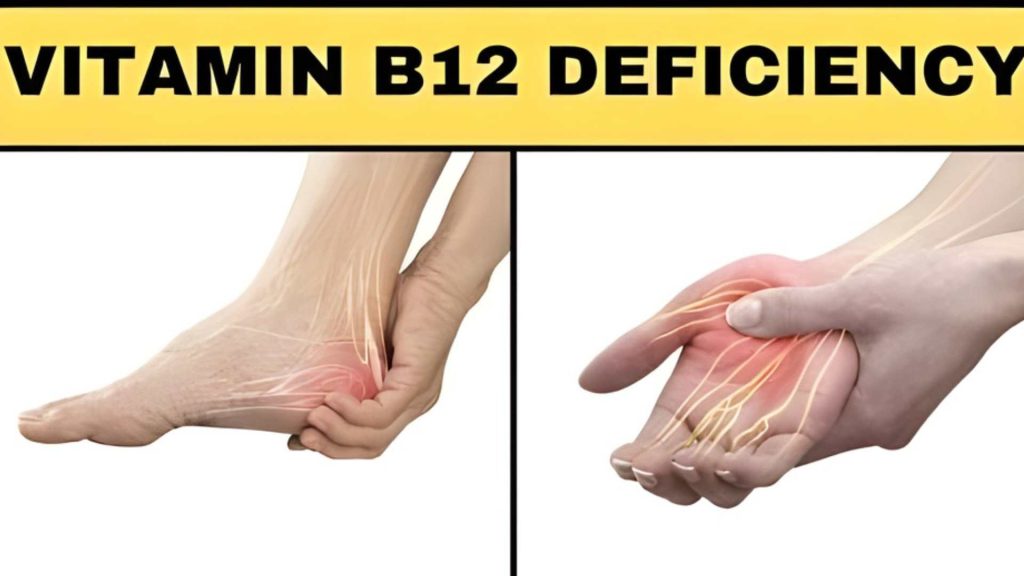
- Vitamin B12 deficiency often develops slowly, but the symptoms can affect daily life significantly.
- Even after getting enough sleep, chronic exhaustion and weakness are common symptoms.
- Many people experience tingling or numbness in the hands and feet, dizziness, and shortness of breath.
- Mental health can also be affected, leading to mood swings, anxiety, irritability, or even depression.
- Mental fog, memory loss, and difficulty focusing are frequently disregarded symptoms that could indicate deficiency of Vitamin B12 levels.
Does Vitamin B12 Deficiency Cause Hair Loss?
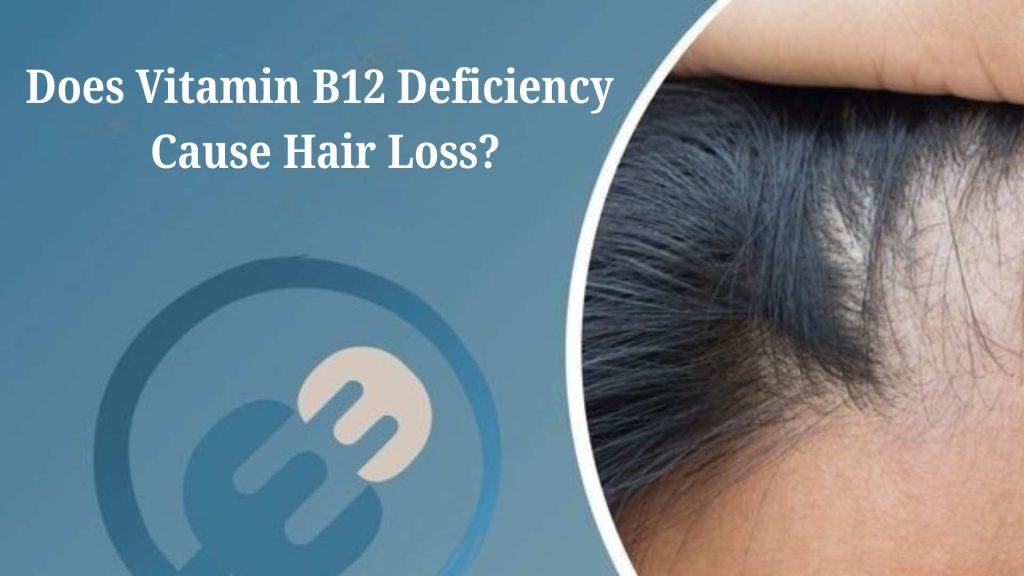
Hair loss due to Vitamin B12 deficiency is often gradual and accompanied by other symptoms like fatigue and pale skin. While hair loss can have many causes, persistent or unexplained shedding may indicate an underlying nutritional deficiency that should not be ignored.
Can Vitamin B12 Deficiency Be a Sign of Cancer?

Certain cancers can interfere with Vitamin B12 absorption by damaging the digestive system. That said, Vitamin B12 deficiency alone does not mean cancer. It simply highlights the importance of medical evaluation when deficiency persists despite treatment, helping rule out serious underlying causes.
How to Recover from Vitamin B12 Deficiency?

Vitamin B12-rich foods include dairy products like milk and curd, eggs, fish, chicken, and meant for non-vegetarians. Fortified foods such as cereals and plant-based milk are helpful for vegetarians. In cases where absorption is poor, doctors may recommend oral supplements or intramuscular injections. Improvement in energy levels is often noticed within weeks, but full recovery may take a few months.
Who is Most at Risk of Vitamin B12 Deficiency?
Certain groups are more vulnerable to Vitamin B12 deficiency. These include vegetarians and vegans, elderly individuals, pregnant and breastfeeding women, people with digestive disorders, and those under chronic physical or mental stress. Regular screening is important for these groups.
How to Maintain Healthy Vitamin B12 Levels
Maintaining healthy Vitamin B12 levels requires a balanced diet that includes reliable sources of the Vitamin. Regular health check-ups can help detect deficiencies early. Supplementation should be done under medical guidance, especially for high-risk individuals. Early detection and timely intervention can prevent long-term complications.
Why Vitamin B12 Deserves More Attention Today
Vitamin B12 plays a vital role in energy, brain health, blood formation, and overall well-being, yet it remains one of the most commonly deficient nutrients in India. Recognising symptoms early and taking proactive steps can make a significant difference in quality of life. With increasing awareness and the right nutritional approach, Vitamin B12 deficiency can be effectively managed, helping individuals stay healthier and more energetic in the long run.







